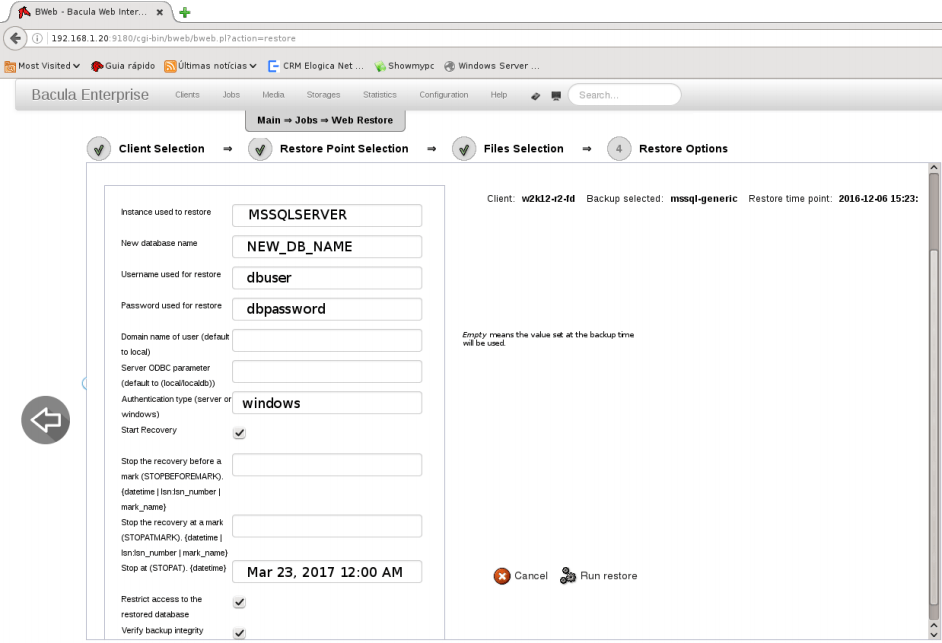
Ripristinare il database SQL con un nuovo nome
Per ripristinare un database con un nuovo nome, potrebbe essere necessario riposizionare i file del database sul disco. Dipende se il database originale è ancora presente.
Se il database originale non è più disponibile, il parametro where o il database “Plugin Options” possono contenere il nuovo nome del database e il plugin gestirà automaticamente la creazione del database con il nuovo nome.
Se il database originale è ancora necessario, il parametro where viene utilizzato per ricollocare i file sul disco e il nuovo nome del database deve essere impostato con il menu “Plugin Options” con l’opzione database. Il layout.dat deve essere selezionato nella struttura di ripristino.
* restore where=c:/tmp replace=always
…
Using Catalog “MyCatalog”
Run Restore job
JobName: RestoreFiles
Bootstrap: /opt/bacula/working/127.0.0.1-dir.restore.1.bsr
Where: c:/tmp
Replace: Always
FileSet: Full Set
Backup Client: win2008-fd
Restore Client: win2008-fd
Storage: File
When: 2015-12-14 09:53:36
Catalog: MyCatalog
Priority: 10
Plugin Options: *None*
OK to run? (yes/mod/no): mod <—————–
Parameters to modify:
1: Level
2: Storage
3: Job
4: FileSet
5: Restore Client
6: When
7: Priority
8: Bootstrap
9: Where
10: File Relocation
11: Replace
12: JobId
13: Plugin Options
Select parameter to modify (1-13): 13 <—————–
Automatically selected : mssql: database=db29187
Plugin Restore Options
instance: *None*
database: *None*
username: *None*
password: *None*
domain: *None*
recovery: *None* (yes)
stop_before_mark: *None*
stop_at_mark: *None*
stop_at: *None*
Use above plugin configuration? (yes/mod/no): mod <——————
You have the following choices:
1: instance (Instance used to restore)
2: database (New database name)
3: username (Username used for restore)
4: password (Password used for restore)
5: domain (Domain name of user (default to local))
6: recovery (Start Recovery)
7: stop_before_mark (Stop the recovery before a mark (STOPBEFOREMARK).
8: stop_at_mark (Stop the recovery at a mark (STOPATMARK).
9: stop_at (Stop at (STOPAT). {datetime})
Select parameter to modify (1-9): 2 <——————
Please enter a value for database: newdb <——————
Use above plugin configuration? (yes/mod/no): yes <——————
Using Catalog “MyCatalog”
Run Restore job
JobName: RestoreFiles
Bootstrap: /opt/bacula/working/127.0.0.1-dir.restore.1.bsr
Where: c:/tmp
Replace: Always
FileSet: Full Set
Backup Client: win2008-fd
Restore Client: win2008-fd
Storage: File
When: 2015-12-14 09:53:36
Catalog: MyCatalog
Priority: 10
Plugin Options: User Specified
OK to run? (yes/mod/no): yes <—————–
Ripristino di SQL su disco locale
Specificando where=c:/path/, i file saranno ripristinati nel filesystem locale e l’amministratore di MS SQL potrà utilizzare un TSQL o la Microsoft SQL Server Mangement Console per ripristinare il database. I comandi SQL necessari per ripristinare il database vengono stampati nell’output del lavoro, come mostrato nel prossimo esempio.
* restore where=c:/tmp
First you select one or more JobIds that contain files
to be restored. You will be presented several methods
of specifying the JobIds. Then you will be allowed to
select which files from those JobIds are to be restored.
To select the JobIds, you have the following choices:
1: List last 20 Jobs run
2: List Jobs where a given File is saved
3: Enter list of comma separated JobIds to select
4: Enter SQL list command
5: Select the most recent backup for a client
6: Select backup for a client before a specified time
7: Enter a list of files to restore
8: Enter a list of files to restore before a specified time
9: Find the JobIds of the most recent backup for a client
10: Find the JobIds for a backup for a client before a specified time
11: Enter a list of directories to restore for found JobIds
12: Select full restore to a specified Job date
13: Cancel
Select item: (1-13): 5
Automatically selected Client: win2008-fd
+——-+——-+———-+———-+———————+—————+
| jobid | level | jobfiles | jobbytes | starttime | volumename |
+——-+——-+———-+———-+———————+—————+
| 1 | F | 3 | 65,771 | 2015-12-14 09:52:31 | TestVolume001 |
| 2 | I | 2 | 65,771 | 2015-12-14 09:52:42 | TestVolume001 |
| 3 | I | 2 | 65,771 | 2015-12-14 09:52:52 | TestVolume001 |
+——-+——-+———-+———-+———————+—————+
You have selected the following JobIds: 1,2,3
Building directory tree for JobId(s) 1,2,3 …
6 files inserted into the tree.
You are now entering file selection mode where you add (mark) and
remove (unmark) files to be restored. No files are initially added, unless
you used the “all” keyword on the command line.
Enter “done” to leave this mode.
cwd is: /
$ cd @mssql
cwd is: /@mssql/
$ cd MSSQLSERVER
cwd is: /@mssql/MSSQLSERVER/
$ m db1684
6 files marked.
$ done
Bootstrap records written to /opt/bacula/working/127.0.0.1-dir.restore.1.bsr
The Job will require the following (*=>InChanger):
Volume(s) Storage(s) SD Device(s)
===========================================================================
TestVolume001 File FileStorage
Volumes marked with “*” are in the Autochanger.
2 files selected to be restored.
Using Catalog “MyCatalog”
Run Restore job
JobName: RestoreFiles
Bootstrap: /opt/bacula/working/127.0.0.1-dir.restore.1.bsr
Where: /tmp
Replace: Always
FileSet: Full Set
Backup Client: win2008-fd
Restore Client: win2008-fd
Storage: File
When: 2015-12-14 09:53:36
Catalog: MyCatalog
Priority: 10
Plugin Options: *None*
OK to run? (yes/mod/no): yes
Job queued. JobId=6
wait
You have messages.
* messages
$ done
17:18 dir JobId 6: Start Restore Job RestoreFiles.2015-12-14_17.18.18_14
17:18 dir JobId 6: Using Device “FileStorage” to read.
17:18 sd JobId 6: Ready to read from volume “TestVolume001” on file device “FileStorage” (/tmp/regress/tmp).
17:18 sd JobId 6: Forward spacing Volume “TestVolume001” to file:block 0:224.
17:18 fd JobId 6: RESTORE DATABASE [db1684] FROM DISK=’c:/tmp/@mssql/MSSQLSERVER/db1684/data.bak’
WITH BLOCKSIZE=65536, BUFFERCOUNT=10, MAXTRANSFERSIZE=65536, NORECOVERY , REPLACE
17:18 fd JobId 6: RESTORE DATABASE [db1684]
FROM DISK=’c:/tmp/@mssql/MSSQLSERVER/db1684/log-34000000014400001.bak’
WITH BLOCKSIZE=65536, BUFFERCOUNT=10, MAXTRANSFERSIZE=65536, NORECOVERY
17:18 fd JobId 6: RESTORE DATABASE [db1684]
FROM DISK=’c:/tmp/@mssql/MSSQLSERVER/db1684/log-34000000018400001.bak’
WITH BLOCKSIZE=65536, BUFFERCOUNT=10, MAXTRANSFERSIZE=65536, NORECOVERY
17:18 fd JobId 6: RESTORE DATABASE [db1684]
FROM DISK=’c:/tmp/@mssql/MSSQLSERVER/db1684/log-34000000029100001.bak’
WITH BLOCKSIZE=65536, BUFFERCOUNT=10, MAXTRANSFERSIZE=65536, NORECOVERY
17:18 sd JobId 6: End of Volume at file 0 on device “FileStorage” (/tmp/regress/tmp), Volume “TestVolume001”
17:18 fd JobId 6: RESTORE DATABASE [db1684]
FROM DISK=’c:/tmp/@mssql/MSSQLSERVER/db1684/log-36000000017200001.bak’
WITH BLOCKSIZE=65536, BUFFERCOUNT=10, MAXTRANSFERSIZE=65536, NORECOVERY
17:18 sd JobId 6: Elapsed time=00:00:01, Transfer rate=9.372 M Bytes/second
17:18 fd JobId 6: RESTORE DATABASE [db1684]
17:18 dir JobId 6: Bacula dir 8.4.8 (22Feb16):
Build OS: x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu archlinux
JobId: 6
Job: RestoreFiles.2015-12-11_17.18.18_14
Restore Client: win2008-fd
Start time: 14-Dec-2015 17:18:20
End time: 14-Dec-2015 17:18:22
Files Expected: 6
Files Restored: 6
Bytes Restored: 9,371,785
Rate: 4685.9 KB/s
FD Errors: 0
FD termination status: OK
SD termination status: OK
Termination: Restore OK
Ripristino del database “master”
Le istruzioni su come fare per ripristinare il database “master” sono dettagliate in questo articolo: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa213839%28v=sql.80%29.aspx
Database in stato di ripristino
Al termine di un ripristino, se l’opzione di recupero del plugin è stata impostata su no, il database ripristinato si troverà nello stato di “restoring”. Per terminare il processo di ripristino, è necessario eseguire il processo di recupero. Può farlo con il seguente comando SQL:
RESTORE [yourdatabase] WITH RECOVERY;